
Understanding GST on Education Services in FY24
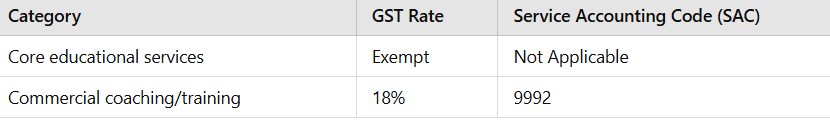
Did you know the government collected a whopping ₹4,792 crore as GST on education services in FY 2023-24? While core education services remain exempt, commercial training and coaching attract 18% GST. Let’s break down what’s taxable and what’s not under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime for education.
GST Collections on Education Services
The Minister of State for Finance, Mr. Pankaj Chaudhary, revealed in Lok Sabha that in FY24, the government collected ₹4,792.4 crore GST from non-exempt educational services. The following highlights the tax structure:
Exemptions for Core Educational Services
Under GST law, specific education services are exempt:
- Services by Educational Institutions:Pre-school to higher secondary education. Courses leading to qualifications recognized by law. Approved vocational courses.
- Support Services to Schools:Transportation for students, staff, and faculty. Catering (including government-sponsored mid-day meals). Security, cleaning, and housekeeping.
- Other Exemptions:Affiliation services provided by educational boards (effective from 10th October 2024). Services for admissions or examinations.
Taxable Education Services
However, not all educational activities escape GST. Commercial training and coaching, considered non-core educational services, attract an 18% GST rate. Other taxable items include:
- Fees for migration and duplicate certificates (unless issued by exempt institutions).
- Coaching institutes and professional skill development programs.
Challenges and Criticism
While core education services enjoy exemptions, critics argue that high GST on commercial education adds financial burdens. Chartered Accountant Ashish Niraj notes:
“The government balances exemptions for core education with GST on commercialized educational activities to maintain fairness while fulfilling its constitutional obligations.”
Nonetheless, with increasing commercialization, calls for expanding exemptions persist, but the GST Council has no immediate plans to extend relief further.
Why GST Matters for Education
The GST structure aims to distinguish between essential and luxury education services. By exempting core services, the government prioritizes affordability and access. Taxing commercial services ensures fair competition and revenue generation to support educational infrastructure.
Education is the backbone of development, and GST policies aim to strike a balance between accessibility and revenue needs. While core education remains tax-free, understanding what attracts GST can help students, parents, and institutions plan better.